1# Zero Allocation JSON Logger
2
3[](https://godoc.org/github.com/rs/zerolog) [](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rs/zerolog/master/LICENSE) [](https://travis-ci.org/rs/zerolog) [](http://gocover.io/github.com/rs/zerolog)
4
5The zerolog package provides a fast and simple logger dedicated to JSON output.
6
7Zerolog's API is designed to provide both a great developer experience and stunning [performance](#benchmarks). Its unique chaining API allows zerolog to write JSON (or CBOR) log events by avoiding allocations and reflection.
8
9Uber's [zap](https://godoc.org/go.uber.org/zap) library pioneered this approach. Zerolog is taking this concept to the next level with a simpler to use API and even better performance.
10
11To keep the code base and the API simple, zerolog focuses on efficient structured logging only. Pretty logging on the console is made possible using the provided (but inefficient) [`zerolog.ConsoleWriter`](#pretty-logging).
12
13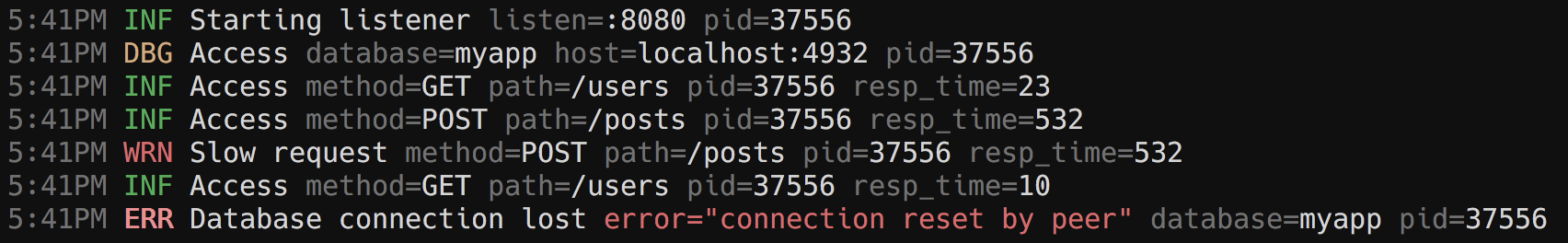
14
15## Who uses zerolog
16
17Find out [who uses zerolog](https://github.com/rs/zerolog/wiki/Who-uses-zerolog) and add your company / project to the list.
18
19## Features
20
21* [Blazing fast](#benchmarks)
22* [Low to zero allocation](#benchmarks)
23* [Leveled logging](#leveled-logging)
24* [Sampling](#log-sampling)
25* [Hooks](#hooks)
26* [Contextual fields](#contextual-logging)
27* `context.Context` integration
28* [Integration with `net/http`](#integration-with-nethttp)
29* [JSON and CBOR encoding formats](#binary-encoding)
30* [Pretty logging for development](#pretty-logging)
31* [Error Logging (with optional Stacktrace)](#error-logging)
32
33## Installation
34
35```bash
36go get -u github.com/rs/zerolog/log
37```
38
39## Getting Started
40
41### Simple Logging Example
42
43For simple logging, import the global logger package **github.com/rs/zerolog/log**
44
45```go
46package main
47
48import (
49 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
50 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
51)
52
53func main() {
54 // UNIX Time is faster and smaller than most timestamps
55 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
56
57 log.Print("hello world")
58}
59
60// Output: {"time":1516134303,"level":"debug","message":"hello world"}
61```
62> Note: By default log writes to `os.Stderr`
63> Note: The default log level for `log.Print` is *debug*
64
65### Contextual Logging
66
67**zerolog** allows data to be added to log messages in the form of key:value pairs. The data added to the message adds "context" about the log event that can be critical for debugging as well as myriad other purposes. An example of this is below:
68
69```go
70package main
71
72import (
73 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
74 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
75)
76
77func main() {
78 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
79
80 log.Debug().
81 Str("Scale", "833 cents").
82 Float64("Interval", 833.09).
83 Msg("Fibonacci is everywhere")
84
85 log.Debug().
86 Str("Name", "Tom").
87 Send()
88}
89
90// Output: {"level":"debug","Scale":"833 cents","Interval":833.09,"time":1562212768,"message":"Fibonacci is everywhere"}
91// Output: {"level":"debug","Name":"Tom","time":1562212768}
92```
93
94> You'll note in the above example that when adding contextual fields, the fields are strongly typed. You can find the full list of supported fields [here](#standard-types)
95
96### Leveled Logging
97
98#### Simple Leveled Logging Example
99
100```go
101package main
102
103import (
104 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
105 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
106)
107
108func main() {
109 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
110
111 log.Info().Msg("hello world")
112}
113
114// Output: {"time":1516134303,"level":"info","message":"hello world"}
115```
116
117> It is very important to note that when using the **zerolog** chaining API, as shown above (`log.Info().Msg("hello world"`), the chain must have either the `Msg` or `Msgf` method call. If you forget to add either of these, the log will not occur and there is no compile time error to alert you of this.
118
119**zerolog** allows for logging at the following levels (from highest to lowest):
120
121* panic (`zerolog.PanicLevel`, 5)
122* fatal (`zerolog.FatalLevel`, 4)
123* error (`zerolog.ErrorLevel`, 3)
124* warn (`zerolog.WarnLevel`, 2)
125* info (`zerolog.InfoLevel`, 1)
126* debug (`zerolog.DebugLevel`, 0)
127* trace (`zerolog.TraceLevel`, -1)
128
129You can set the Global logging level to any of these options using the `SetGlobalLevel` function in the zerolog package, passing in one of the given constants above, e.g. `zerolog.InfoLevel` would be the "info" level. Whichever level is chosen, all logs with a level greater than or equal to that level will be written. To turn off logging entirely, pass the `zerolog.Disabled` constant.
130
131#### Setting Global Log Level
132
133This example uses command-line flags to demonstrate various outputs depending on the chosen log level.
134
135```go
136package main
137
138import (
139 "flag"
140
141 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
142 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
143)
144
145func main() {
146 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
147 debug := flag.Bool("debug", false, "sets log level to debug")
148
149 flag.Parse()
150
151 // Default level for this example is info, unless debug flag is present
152 zerolog.SetGlobalLevel(zerolog.InfoLevel)
153 if *debug {
154 zerolog.SetGlobalLevel(zerolog.DebugLevel)
155 }
156
157 log.Debug().Msg("This message appears only when log level set to Debug")
158 log.Info().Msg("This message appears when log level set to Debug or Info")
159
160 if e := log.Debug(); e.Enabled() {
161 // Compute log output only if enabled.
162 value := "bar"
163 e.Str("foo", value).Msg("some debug message")
164 }
165}
166```
167
168Info Output (no flag)
169
170```bash
171$ ./logLevelExample
172{"time":1516387492,"level":"info","message":"This message appears when log level set to Debug or Info"}
173```
174
175Debug Output (debug flag set)
176
177```bash
178$ ./logLevelExample -debug
179{"time":1516387573,"level":"debug","message":"This message appears only when log level set to Debug"}
180{"time":1516387573,"level":"info","message":"This message appears when log level set to Debug or Info"}
181{"time":1516387573,"level":"debug","foo":"bar","message":"some debug message"}
182```
183
184#### Logging without Level or Message
185
186You may choose to log without a specific level by using the `Log` method. You may also write without a message by setting an empty string in the `msg string` parameter of the `Msg` method. Both are demonstrated in the example below.
187
188```go
189package main
190
191import (
192 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
193 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
194)
195
196func main() {
197 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
198
199 log.Log().
200 Str("foo", "bar").
201 Msg("")
202}
203
204// Output: {"time":1494567715,"foo":"bar"}
205```
206
207### Error Logging
208
209You can log errors using the `Err` method
210
211```go
212package main
213
214import (
215 "errors"
216
217 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
218 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
219)
220
221func main() {
222 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
223
224 err := errors.New("seems we have an error here")
225 log.Error().Err(err).Msg("")
226}
227
228// Output: {"level":"error","error":"seems we have an error here","time":1609085256}
229```
230
231> The default field name for errors is `error`, you can change this by setting `zerolog.ErrorFieldName` to meet your needs.
232
233#### Error Logging with Stacktrace
234
235Using `github.com/pkg/errors`, you can add a formatted stacktrace to your errors.
236
237```go
238package main
239
240import (
241 "github.com/pkg/errors"
242 "github.com/rs/zerolog/pkgerrors"
243
244 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
245 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
246)
247
248func main() {
249 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
250 zerolog.ErrorStackMarshaler = pkgerrors.MarshalStack
251
252 err := outer()
253 log.Error().Stack().Err(err).Msg("")
254}
255
256func inner() error {
257 return errors.New("seems we have an error here")
258}
259
260func middle() error {
261 err := inner()
262 if err != nil {
263 return err
264 }
265 return nil
266}
267
268func outer() error {
269 err := middle()
270 if err != nil {
271 return err
272 }
273 return nil
274}
275
276// Output: {"level":"error","stack":[{"func":"inner","line":"20","source":"errors.go"},{"func":"middle","line":"24","source":"errors.go"},{"func":"outer","line":"32","source":"errors.go"},{"func":"main","line":"15","source":"errors.go"},{"func":"main","line":"204","source":"proc.go"},{"func":"goexit","line":"1374","source":"asm_amd64.s"}],"error":"seems we have an error here","time":1609086683}
277```
278
279> zerolog.ErrorStackMarshaler must be set in order for the stack to output anything.
280
281#### Logging Fatal Messages
282
283```go
284package main
285
286import (
287 "errors"
288
289 "github.com/rs/zerolog"
290 "github.com/rs/zerolog/log"
291)
292
293func main() {
294 err := errors.New("A repo man spends his life getting into tense situations")
295 service := "myservice"
296
297 zerolog.TimeFieldFormat = zerolog.TimeFormatUnix
298
299 log.Fatal().
300 Err(err).
301 Str("service", service).
302 Msgf("Cannot start %s", service)
303}
304
305// Output: {"time":1516133263,"level":"fatal","error":"A repo man spends his life getting into tense situations","service":"myservice","message":"Cannot start myservice"}
306// exit status 1
307```
308
309> NOTE: Using `Msgf` generates one allocation even when the logger is disabled.
310
311
312### Create logger instance to manage different outputs
313
314```go
315logger := zerolog.New(os.Stderr).With().Timestamp().Logger()
316
317logger.Info().Str("foo", "bar").Msg("hello world")
318
319// Output: {"level":"info","time":1494567715,"message":"hello world","foo":"bar"}
320```
321
322### Sub-loggers let you chain loggers with additional context
323
324```go
325sublogger := log.With().
326 Str("component", "foo").
327 Logger()
328sublogger.Info().Msg("hello world")
329
330// Output: {"level":"info","time":1494567715,"message":"hello world","component":"foo"}
331```
332
333### Pretty logging
334
335To log a human-friendly, colorized output, use `zerolog.ConsoleWriter`:
336
337```go
338log.Logger = log.Output(zerolog.ConsoleWriter{Out: os.Stderr})
339
340log.Info().Str("foo", "bar").Msg("Hello world")
341
342// Output: 3:04PM INF Hello World foo=bar
343```
344
345To customize the configuration and formatting:
346
347```go
348output := zerolog.ConsoleWriter{Out: os.Stdout, TimeFormat: time.RFC3339}
349output.FormatLevel = func(i interface{}) string {
350 return strings.ToUpper(fmt.Sprintf("| %-6s|", i))
351}
352output.FormatMessage = func(i interface{}) string {
353 return fmt.Sprintf("***%s****", i)
354}
355output.FormatFieldName = func(i interface{}) string {
356 return fmt.Sprintf("%s:", i)
357}
358output.FormatFieldValue = func(i interface{}) string {
359 return strings.ToUpper(fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
360}
361
362log := zerolog.New(output).With().Timestamp().Logger()
363
364log.Info().Str("foo", "bar").Msg("Hello World")
365
366// Output: 2006-01-02T15:04:05Z07:00 | INFO | ***Hello World**** foo:BAR
367```
368
369### Sub dictionary
370
371```go
372log.Info().
373 Str("foo", "bar").
374 Dict("dict", zerolog.Dict().
375 Str("bar", "baz").
376 Int("n", 1),
377 ).Msg("hello world")
378
379// Output: {"level":"info","time":1494567715,"foo":"bar","dict":{"bar":"baz","n":1},"message":"hello world"}
380```
381
382### Customize automatic field names
383
384```go
385zerolog.TimestampFieldName = "t"
386zerolog.LevelFieldName = "l"
387zerolog.MessageFieldName = "m"
388
389log.Info().Msg("hello world")
390
391// Output: {"l":"info","t":1494567715,"m":"hello world"}
392```
393
394### Add contextual fields to the global logger
395
396```go
397log.Logger = log.With().Str("foo", "bar").Logger()
398```
399
400### Add file and line number to log
401
402Equivalent of `Llongfile`:
403
404```go
405log.Logger = log.With().Caller().Logger()
406log.Info().Msg("hello world")
407
408// Output: {"level": "info", "message": "hello world", "caller": "/go/src/your_project/some_file:21"}
409```
410
411Equivalent of `Lshortfile`:
412
413```go
414zerolog.CallerMarshalFunc = func(file string, line int) string {
415 short := file
416 for i := len(file) - 1; i > 0; i-- {
417 if file[i] == '/' {
418 short = file[i+1:]
419 break
420 }
421 }
422 file = short
423 return file + ":" + strconv.Itoa(line)
424}
425log.Logger = log.With().Caller().Logger()
426log.Info().Msg("hello world")
427
428// Output: {"level": "info", "message": "hello world", "caller": "some_file:21"}
429```
430
431### Thread-safe, lock-free, non-blocking writer
432
433If your writer might be slow or not thread-safe and you need your log producers to never get slowed down by a slow writer, you can use a `diode.Writer` as follows:
434
435```go
436wr := diode.NewWriter(os.Stdout, 1000, 10*time.Millisecond, func(missed int) {
437 fmt.Printf("Logger Dropped %d messages", missed)
438 })
439log := zerolog.New(wr)
440log.Print("test")
441```
442
443You will need to install `code.cloudfoundry.org/go-diodes` to use this feature.
444
445### Log Sampling
446
447```go
448sampled := log.Sample(&zerolog.BasicSampler{N: 10})
449sampled.Info().Msg("will be logged every 10 messages")
450
451// Output: {"time":1494567715,"level":"info","message":"will be logged every 10 messages"}
452```
453
454More advanced sampling:
455
456```go
457// Will let 5 debug messages per period of 1 second.
458// Over 5 debug message, 1 every 100 debug messages are logged.
459// Other levels are not sampled.
460sampled := log.Sample(zerolog.LevelSampler{
461 DebugSampler: &zerolog.BurstSampler{
462 Burst: 5,
463 Period: 1*time.Second,
464 NextSampler: &zerolog.BasicSampler{N: 100},
465 },
466})
467sampled.Debug().Msg("hello world")
468
469// Output: {"time":1494567715,"level":"debug","message":"hello world"}
470```
471
472### Hooks
473
474```go
475type SeverityHook struct{}
476
477func (h SeverityHook) Run(e *zerolog.Event, level zerolog.Level, msg string) {
478 if level != zerolog.NoLevel {
479 e.Str("severity", level.String())
480 }
481}
482
483hooked := log.Hook(SeverityHook{})
484hooked.Warn().Msg("")
485
486// Output: {"level":"warn","severity":"warn"}
487```
488
489### Pass a sub-logger by context
490
491```go
492ctx := log.With().Str("component", "module").Logger().WithContext(ctx)
493
494log.Ctx(ctx).Info().Msg("hello world")
495
496// Output: {"component":"module","level":"info","message":"hello world"}
497```
498
499### Set as standard logger output
500
501```go
502log := zerolog.New(os.Stdout).With().
503 Str("foo", "bar").
504 Logger()
505
506stdlog.SetFlags(0)
507stdlog.SetOutput(log)
508
509stdlog.Print("hello world")
510
511// Output: {"foo":"bar","message":"hello world"}
512```
513
514### Integration with `net/http`
515
516The `github.com/rs/zerolog/hlog` package provides some helpers to integrate zerolog with `http.Handler`.
517
518In this example we use [alice](https://github.com/justinas/alice) to install logger for better readability.
519
520```go
521log := zerolog.New(os.Stdout).With().
522 Timestamp().
523 Str("role", "my-service").
524 Str("host", host).
525 Logger()
526
527c := alice.New()
528
529// Install the logger handler with default output on the console
530c = c.Append(hlog.NewHandler(log))
531
532// Install some provided extra handler to set some request's context fields.
533// Thanks to that handler, all our logs will come with some prepopulated fields.
534c = c.Append(hlog.AccessHandler(func(r *http.Request, status, size int, duration time.Duration) {
535 hlog.FromRequest(r).Info().
536 Str("method", r.Method).
537 Stringer("url", r.URL).
538 Int("status", status).
539 Int("size", size).
540 Dur("duration", duration).
541 Msg("")
542}))
543c = c.Append(hlog.RemoteAddrHandler("ip"))
544c = c.Append(hlog.UserAgentHandler("user_agent"))
545c = c.Append(hlog.RefererHandler("referer"))
546c = c.Append(hlog.RequestIDHandler("req_id", "Request-Id"))
547
548// Here is your final handler
549h := c.Then(http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
550 // Get the logger from the request's context. You can safely assume it
551 // will be always there: if the handler is removed, hlog.FromRequest
552 // will return a no-op logger.
553 hlog.FromRequest(r).Info().
554 Str("user", "current user").
555 Str("status", "ok").
556 Msg("Something happened")
557
558 // Output: {"level":"info","time":"2001-02-03T04:05:06Z","role":"my-service","host":"local-hostname","req_id":"b4g0l5t6tfid6dtrapu0","user":"current user","status":"ok","message":"Something happened"}
559}))
560http.Handle("/", h)
561
562if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
563 log.Fatal().Err(err).Msg("Startup failed")
564}
565```
566
567## Multiple Log Output
568`zerolog.MultiLevelWriter` may be used to send the log message to multiple outputs.
569In this example, we send the log message to both `os.Stdout` and the in-built ConsoleWriter.
570```go
571func main() {
572 consoleWriter := zerolog.ConsoleWriter{Out: os.Stdout}
573
574 multi := zerolog.MultiLevelWriter(consoleWriter, os.Stdout)
575
576 logger := zerolog.New(multi).With().Timestamp().Logger()
577
578 logger.Info().Msg("Hello World!")
579}
580
581// Output (Line 1: Console; Line 2: Stdout)
582// 12:36PM INF Hello World!
583// {"level":"info","time":"2019-11-07T12:36:38+03:00","message":"Hello World!"}
584```
585
586## Global Settings
587
588Some settings can be changed and will be applied to all loggers:
589
590* `log.Logger`: You can set this value to customize the global logger (the one used by package level methods).
591* `zerolog.SetGlobalLevel`: Can raise the minimum level of all loggers. Call this with `zerolog.Disabled` to disable logging altogether (quiet mode).
592* `zerolog.DisableSampling`: If argument is `true`, all sampled loggers will stop sampling and issue 100% of their log events.
593* `zerolog.TimestampFieldName`: Can be set to customize `Timestamp` field name.
594* `zerolog.LevelFieldName`: Can be set to customize level field name.
595* `zerolog.MessageFieldName`: Can be set to customize message field name.
596* `zerolog.ErrorFieldName`: Can be set to customize `Err` field name.
597* `zerolog.TimeFieldFormat`: Can be set to customize `Time` field value formatting. If set with `zerolog.TimeFormatUnix`, `zerolog.TimeFormatUnixMs` or `zerolog.TimeFormatUnixMicro`, times are formated as UNIX timestamp.
598* `zerolog.DurationFieldUnit`: Can be set to customize the unit for time.Duration type fields added by `Dur` (default: `time.Millisecond`).
599* `zerolog.DurationFieldInteger`: If set to `true`, `Dur` fields are formatted as integers instead of floats (default: `false`).
600* `zerolog.ErrorHandler`: Called whenever zerolog fails to write an event on its output. If not set, an error is printed on the stderr. This handler must be thread safe and non-blocking.
601
602## Field Types
603
604### Standard Types
605
606* `Str`
607* `Bool`
608* `Int`, `Int8`, `Int16`, `Int32`, `Int64`
609* `Uint`, `Uint8`, `Uint16`, `Uint32`, `Uint64`
610* `Float32`, `Float64`
611
612### Advanced Fields
613
614* `Err`: Takes an `error` and renders it as a string using the `zerolog.ErrorFieldName` field name.
615* `Func`: Run a `func` only if the level is enabled.
616* `Timestamp`: Inserts a timestamp field with `zerolog.TimestampFieldName` field name, formatted using `zerolog.TimeFieldFormat`.
617* `Time`: Adds a field with time formatted with `zerolog.TimeFieldFormat`.
618* `Dur`: Adds a field with `time.Duration`.
619* `Dict`: Adds a sub-key/value as a field of the event.
620* `RawJSON`: Adds a field with an already encoded JSON (`[]byte`)
621* `Hex`: Adds a field with value formatted as a hexadecimal string (`[]byte`)
622* `Interface`: Uses reflection to marshal the type.
623
624Most fields are also available in the slice format (`Strs` for `[]string`, `Errs` for `[]error` etc.)
625
626## Binary Encoding
627
628In addition to the default JSON encoding, `zerolog` can produce binary logs using [CBOR](https://cbor.io) encoding. The choice of encoding can be decided at compile time using the build tag `binary_log` as follows:
629
630```bash
631go build -tags binary_log .
632```
633
634To Decode binary encoded log files you can use any CBOR decoder. One has been tested to work
635with zerolog library is [CSD](https://github.com/toravir/csd/).
636
637## Related Projects
638
639* [grpc-zerolog](https://github.com/cheapRoc/grpc-zerolog): Implementation of `grpclog.LoggerV2` interface using `zerolog`
640* [overlog](https://github.com/Trendyol/overlog): Implementation of `Mapped Diagnostic Context` interface using `zerolog`
641* [zerologr](https://github.com/go-logr/zerologr): Implementation of `logr.LogSink` interface using `zerolog`
642
643## Benchmarks
644
645See [logbench](http://hackemist.com/logbench/) for more comprehensive and up-to-date benchmarks.
646
647All operations are allocation free (those numbers *include* JSON encoding):
648
649```text
650BenchmarkLogEmpty-8 100000000 19.1 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
651BenchmarkDisabled-8 500000000 4.07 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
652BenchmarkInfo-8 30000000 42.5 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
653BenchmarkContextFields-8 30000000 44.9 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
654BenchmarkLogFields-8 10000000 184 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
655```
656
657There are a few Go logging benchmarks and comparisons that include zerolog.
658
659* [imkira/go-loggers-bench](https://github.com/imkira/go-loggers-bench)
660* [uber-common/zap](https://github.com/uber-go/zap#performance)
661
662Using Uber's zap comparison benchmark:
663
664Log a message and 10 fields:
665
666| Library | Time | Bytes Allocated | Objects Allocated |
667| :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
668| zerolog | 767 ns/op | 552 B/op | 6 allocs/op |
669| :zap: zap | 848 ns/op | 704 B/op | 2 allocs/op |
670| :zap: zap (sugared) | 1363 ns/op | 1610 B/op | 20 allocs/op |
671| go-kit | 3614 ns/op | 2895 B/op | 66 allocs/op |
672| lion | 5392 ns/op | 5807 B/op | 63 allocs/op |
673| logrus | 5661 ns/op | 6092 B/op | 78 allocs/op |
674| apex/log | 15332 ns/op | 3832 B/op | 65 allocs/op |
675| log15 | 20657 ns/op | 5632 B/op | 93 allocs/op |
676
677Log a message with a logger that already has 10 fields of context:
678
679| Library | Time | Bytes Allocated | Objects Allocated |
680| :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
681| zerolog | 52 ns/op | 0 B/op | 0 allocs/op |
682| :zap: zap | 283 ns/op | 0 B/op | 0 allocs/op |
683| :zap: zap (sugared) | 337 ns/op | 80 B/op | 2 allocs/op |
684| lion | 2702 ns/op | 4074 B/op | 38 allocs/op |
685| go-kit | 3378 ns/op | 3046 B/op | 52 allocs/op |
686| logrus | 4309 ns/op | 4564 B/op | 63 allocs/op |
687| apex/log | 13456 ns/op | 2898 B/op | 51 allocs/op |
688| log15 | 14179 ns/op | 2642 B/op | 44 allocs/op |
689
690Log a static string, without any context or `printf`-style templating:
691
692| Library | Time | Bytes Allocated | Objects Allocated |
693| :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
694| zerolog | 50 ns/op | 0 B/op | 0 allocs/op |
695| :zap: zap | 236 ns/op | 0 B/op | 0 allocs/op |
696| standard library | 453 ns/op | 80 B/op | 2 allocs/op |
697| :zap: zap (sugared) | 337 ns/op | 80 B/op | 2 allocs/op |
698| go-kit | 508 ns/op | 656 B/op | 13 allocs/op |
699| lion | 771 ns/op | 1224 B/op | 10 allocs/op |
700| logrus | 1244 ns/op | 1505 B/op | 27 allocs/op |
701| apex/log | 2751 ns/op | 584 B/op | 11 allocs/op |
702| log15 | 5181 ns/op | 1592 B/op | 26 allocs/op |
703
704## Caveats
705
706Note that zerolog does no de-duplication of fields. Using the same key multiple times creates multiple keys in final JSON:
707
708```go
709logger := zerolog.New(os.Stderr).With().Timestamp().Logger()
710logger.Info().
711 Timestamp().
712 Msg("dup")
713// Output: {"level":"info","time":1494567715,"time":1494567715,"message":"dup"}
714```
715
716In this case, many consumers will take the last value, but this is not guaranteed; check yours if in doubt.
View as plain text