1# grpc-gateway
2
3[](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/releases)
4[](https://circleci.com/gh/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway)
5[](https://codecov.io/gh/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway)
6[](LICENSE.txt)
7[](https://join.slack.com/t/gophers/shared_invite/zt-gmw97q11-1OWgj2Dqsc13eqoSPwvNDQ)
8
9The grpc-gateway is a plugin of the Google protocol buffers compiler
10[protoc](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf).
11It reads protobuf service definitions and generates a reverse-proxy server which
12translates a RESTful HTTP API into gRPC. This server is generated according to the
13[`google.api.http`](https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/blob/master/google/api/http.proto#L46)
14annotations in your service definitions.
15
16This helps you provide your APIs in both gRPC and RESTful style at the same time.
17
18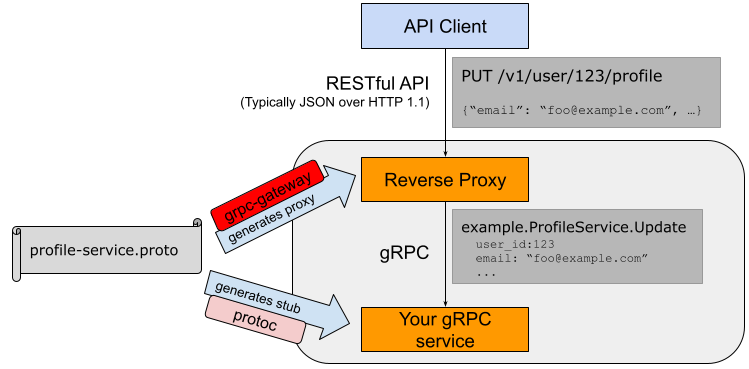
19
20## Testimonials
21
22 > We use the gRPC-Gateway to serve millions of API requests per day,
23 and have been since 2018, and through all of that,
24 we have never had any issues with it.
25>
26> _- William Mill, [Ad Hoc](http://adhocteam.us/)_
27
28## Check out our [documentation](https://grpc-ecosystem.github.io/grpc-gateway/)!
29
30## Background
31gRPC is great -- it generates API clients and server stubs in many programming
32languages, it is fast, easy-to-use, bandwidth-efficient and its design is
33combat-proven by Google. However, you might still want to provide a traditional
34RESTful JSON API as well. Reasons can range from maintaining
35backward-compatibility, supporting languages or clients that are not well supported by
36gRPC, to simply maintaining the aesthetics and tooling involved with a RESTful
37JSON architecture.
38
39This project aims to provide that HTTP+JSON interface to your gRPC service.
40A small amount of configuration in your service to attach HTTP semantics is all
41that's needed to generate a reverse-proxy with this library.
42
43## Installation
44
45The grpc-gateway requires a local installation of the Google protocol buffers
46compiler `protoc` v3.0.0 or above. Please install this via your local package
47manager or by downloading one of the releases from the official repository:
48
49https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases
50
51The following instructions assume you are using
52[Go Modules](https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/Modules) for dependency
53management. Use a
54[tool dependency](https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/Modules#how-can-i-track-tool-dependencies-for-a-module)
55to track the versions of the following executable packages:
56
57```go
58// +build tools
59
60package tools
61
62import (
63 _ "github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway"
64 _ "github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger"
65 _ "github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go"
66)
67```
68
69Run `go mod tidy` to resolve the versions. Install by running
70
71```sh
72$ go install \
73 github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway \
74 github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger \
75 github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
76```
77
78This will place three binaries in your `$GOBIN`;
79
80* `protoc-gen-grpc-gateway`
81* `protoc-gen-swagger`
82* `protoc-gen-go`
83
84Make sure that your `$GOBIN` is in your `$PATH`.
85
86## Usage
87
881. Define your [gRPC](https://grpc.io/docs/) service using protocol buffers
89
90 `your_service.proto`:
91 ```protobuf
92 syntax = "proto3";
93 package example;
94 message StringMessage {
95 string value = 1;
96 }
97
98 service YourService {
99 rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
100 }
101 ```
102
1032. Generate gRPC stubs
104
105 This step generates the gRPC stubs that you can use to implement the service and consume from clients:
106
107 Here's an example of what a `protoc` command might look like to generate Go stubs:
108
109 ```sh
110 protoc -I . --go_out ./gen/go/ --go_opt plugins=grpc --go_opt paths=source_relative your/service/v1/your_service.proto
111 ```
112
1133. Implement your service in gRPC as usual
114
115 1. (Optional) Generate gRPC stub in the [other programming languages](https://grpc.io/docs/).
116
117 For example, the following generates gRPC code for Ruby based on `your/service/v1/your_service.proto`:
118 ```sh
119 protoc -I . --ruby_out ./gen/ruby your/service/v1/your_service.proto
120
121 protoc -I . --grpc-ruby_out ./gen/ruby your/service/v1/your_service.proto
122 ```
123 2. Add the googleapis-common-protos gem (or your language equivalent) as a dependency to your project.
124 3. Implement your gRPC service stubs
125
1264. Generate reverse-proxy using `protoc-gen-grpc-gateway`
127
128 At this point, you have 3 options:
129
130 * no further modifications, use the default mapping to HTTP semantics (method, path, etc.)
131 * this will work on any `.proto` file, but will not allow setting HTTP paths, request parameters or similar
132 * additional `.proto` modifications to use a custom mapping
133 * relies on parameters in the `.proto` file to set custom HTTP mappings
134 * no `.proto` modifications, but use an external configuration file
135 * relies on an external configuration file to set custom HTTP mappings
136 * mostly useful when the source proto file isn't under your control
137
138 1. Using the default mapping
139
140 This requires no additional modification to the `.proto` file, but does require enabling a specific option when executing the plugin.
141 The `generate_unbound_methods` should be enabled.
142
143 Here's what a `protoc` execution might look like with this option enabled:
144
145 ```sh
146 protoc -I . --grpc-gateway_out ./gen/go \
147 --grpc-gateway_opt logtostderr=true \
148 --grpc-gateway_opt paths=source_relative \
149 --grpc-gateway_opt generate_unbound_methods=true \
150 your/service/v1/your_service.proto
151 ```
152
153 2. With custom annotations
154
155 Add a [`google.api.http`](https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/blob/master/google/api/http.proto#L46)
156 annotation to your .proto file
157
158 `your_service.proto`:
159 ```diff
160 syntax = "proto3";
161 package example;
162 +
163 +import "google/api/annotations.proto";
164 +
165 message StringMessage {
166 string value = 1;
167 }
168
169 service YourService {
170 - rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
171 + rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
172 + option (google.api.http) = {
173 + post: "/v1/example/echo"
174 + body: "*"
175 + };
176 + }
177 }
178 ```
179
180 >You will need to provide the required third party protobuf files to the `protoc` compiler.
181 >They are included in this repo under the `third_party/googleapis` folder, and we recommend copying
182 >them into your `protoc` generation file structure. If you've structured your proto files according
183 >to something like [the Buf style guide](https://buf.build/docs/style-guide#files-and-packages),
184 >you could copy the files into a top-level `./google` folder.
185
186 See [a_bit_of_everything.proto](examples/internal/proto/examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.proto)
187 for examples of more annotations you can add to customize gateway behavior
188 and generated Swagger output.
189
190 Here's what a `protoc` execution might look like:
191
192 ```sh
193 protoc -I . --grpc-gateway_out ./gen/go \
194 --grpc-gateway_opt logtostderr=true \
195 --grpc-gateway_opt paths=source_relative \
196 your/service/v1/your_service.proto
197 ```
198
199 3. External configuration
200 If you do not want to (or cannot) modify the proto file for use with grpc-gateway you can
201 alternatively use an external
202 [gRPC Service Configuration](https://cloud.google.com/endpoints/docs/grpc/grpc-service-config) file.
203 [Check our documentation](https://grpc-ecosystem.github.io/grpc-gateway/docs/grpcapiconfiguration.html)
204 for more information.
205
206 Here's what a `protoc` execution might look like with this option enabled:
207
208 ```sh
209 protoc -I . --grpc-gateway_out ./gen/go \
210 --grpc-gateway_opt logtostderr=true \
211 --grpc-gateway_opt paths=source_relative \
212 --grpc-gateway_opt grpc_api_configuration=path/to/config.yaml \
213 your/service/v1/your_service.proto
214 ```
215
2165. Write an entrypoint for the HTTP reverse-proxy server
217
218 ```go
219 package main
220
221 import (
222 "context"
223 "flag"
224 "net/http"
225
226 "github.com/golang/glog"
227 "github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
228 "google.golang.org/grpc"
229
230 gw "github.com/yourorg/yourrepo/proto/gen/go/your/service/v1/your_service" // Update
231 )
232
233 var (
234 // command-line options:
235 // gRPC server endpoint
236 grpcServerEndpoint = flag.String("grpc-server-endpoint", "localhost:9090", "gRPC server endpoint")
237 )
238
239 func run() error {
240 ctx := context.Background()
241 ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
242 defer cancel()
243
244 // Register gRPC server endpoint
245 // Note: Make sure the gRPC server is running properly and accessible
246 mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
247 opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()}
248 err := gw.RegisterYourServiceHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, *grpcServerEndpoint, opts)
249 if err != nil {
250 return err
251 }
252
253 // Start HTTP server (and proxy calls to gRPC server endpoint)
254 return http.ListenAndServe(":8081", mux)
255 }
256
257 func main() {
258 flag.Parse()
259 defer glog.Flush()
260
261 if err := run(); err != nil {
262 glog.Fatal(err)
263 }
264 }
265 ```
266
2676. (Optional) Generate swagger definitions using `protoc-gen-swagger`
268
269 ```sh
270 protoc -I . --swagger_out ./gen/swagger --swagger_opt logtostderr=true your/service/v1/your_service.proto
271 ```
272
273 Note that this plugin also supports generating swagger definitions for unannotated methods; use the `generate_unbound_methods` option to enable this.
274
275## Video intro
276
277This GopherCon UK 2019 presentation from our maintainer
278[@JohanBrandhorst](https://github.com/johanbrandhorst) provides a good intro to
279using the grpc-gateway. It uses the following boilerplate repo as a base:
280https://github.com/johanbrandhorst/grpc-gateway-boilerplate.
281
282[](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pq1paKC-fXk)
283
284## Parameters and flags
285
286During code generation with `protoc`, flags to grpc-gateway tools must be passed
287through protoc using one of 2 patterns:
288
289* as part of the `--<tool_suffix>_out` `protoc` parameter: `--<tool_suffix>_out=<flags>:<path>`
290
291```sh
292--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true,repeated_path_param_separator=ssv:.
293--swagger_out=logtostderr=true,repeated_path_param_separator=ssv:.
294```
295
296* using additional `--<tool_suffix>_opt` parameters: `--<tool_suffix>_opt=<flag>[,<flag>]*`
297
298```sh
299--grpc-gateway_opt logtostderr=true,repeated_path_param_separator=ssv
300# or separately
301--grpc-gateway_opt logtostderr=true --grpc-gateway_opt repeated_path_param_separator=ssv
302
303--swagger_opt logtostderr=true,repeated_path_param_separator=ssv
304# or separately
305--swagger_opt logtostderr=true --swagger_opt repeated_path_param_separator=ssv
306```
307
308`protoc-gen-grpc-gateway` supports custom mapping from Protobuf `import` to
309Golang import paths. They are compatible with
310[the parameters with the same names in `protoc-gen-go`](https://github.com/golang/protobuf#parameters).
311
312In addition we also support the `request_context` parameter in order to use the
313`http.Request`'s Context (only for Go 1.7 and above). This parameter can be
314useful to pass the request-scoped context between the gateway and the gRPC service.
315
316`protoc-gen-grpc-gateway` also supports some more command line flags to control
317logging. You can give these flags together with parameters above. Run
318`protoc-gen-grpc-gateway --help` for more details about the flags.
319
320Similarly, `protoc-gen-swagger` supports command-line flags to control Swagger
321output (for example, `json_names_for_fields` to output JSON names for fields
322instead of protobuf names). Run `protoc-gen-swagger --help` for more flag
323details. Further Swagger customization is possible by annotating your `.proto`
324files with options from
325[openapiv2.proto](protoc-gen-swagger/options/openapiv2.proto) - see
326[a_bit_of_everything.proto](examples/internal/proto/examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.proto)
327for examples.
328
329## More Examples
330More examples are available under `examples` directory.
331* `proto/examplepb/echo_service.proto`, `proto/examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.proto`, `proto/examplepb/unannotated_echo_service.proto`: service definition
332 * `proto/examplepb/echo_service.pb.go`, `proto/examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.pb.go`, `proto/examplepb/unannotated_echo_service.pb.go`: [generated] stub of the service
333 * `proto/examplepb/echo_service.pb.gw.go`, `proto/examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.pb.gw.go`, `proto/examplepb/uannotated_echo_service.pb.gw.go`: [generated] reverse proxy for the service
334 * `proto/examplepb/unannotated_echo_service.yaml`: gRPC API Configuration for ```unannotated_echo_service.proto```
335* `server/main.go`: service implementation
336* `main.go`: entrypoint of the generated reverse proxy
337
338To use the same port for custom HTTP handlers (e.g. serving `swagger.json`),
339gRPC-gateway, and a gRPC server, see
340[this example by CoreOS](https://github.com/philips/grpc-gateway-example/blob/master/cmd/serve.go)
341(and its accompanying [blog post](https://coreos.com/blog/grpc-protobufs-swagger.html)).
342
343## Features
344
345### Supported
346
347* Generating JSON API handlers.
348* Method parameters in the request body.
349* Method parameters in the request path.
350* Method parameters in query string.
351* Enum fields in the path parameter (including repeated enum fields).
352* Mapping streaming APIs to newline-delimited JSON streams.
353* Mapping HTTP headers with `Grpc-Metadata-` prefix to gRPC metadata (prefixed with `grpcgateway-`)
354* Optionally emitting API definitions for
355[OpenAPI (Swagger) v2](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/2-0/basic-structure/).
356* Setting [gRPC timeouts](https://github.com/grpc/grpc/blob/master/doc/PROTOCOL-HTTP2.md#requests)
357through inbound HTTP `Grpc-Timeout` header.
358* Partial support for [gRPC API Configuration](https://cloud.google.com/endpoints/docs/grpc/grpc-service-config)
359files as an alternative to annotation.
360* Automatically translating PATCH requests into Field Mask gRPC requests. See
361[the docs](https://grpc-ecosystem.github.io/grpc-gateway/docs/patch.html)
362for more information.
363
364### No plan to support
365But patch is welcome.
366* Method parameters in HTTP headers.
367* Handling trailer metadata.
368* Encoding request/response body in XML.
369* True bi-directional streaming.
370
371# Mapping gRPC to HTTP
372
373* [How gRPC error codes map to HTTP status codes in the response](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/runtime/errors.go#L15).
374* HTTP request source IP is added as `X-Forwarded-For` gRPC request header.
375* HTTP request host is added as `X-Forwarded-Host` gRPC request header.
376* HTTP `Authorization` header is added as `authorization` gRPC request header.
377* Remaining Permanent HTTP header keys (as specified by the IANA
378[here](http://www.iana.org/assignments/message-headers/message-headers.xhtml)
379are prefixed with `grpcgateway-` and added with their values to gRPC request
380header.
381* HTTP headers that start with 'Grpc-Metadata-' are mapped to gRPC metadata
382(prefixed with `grpcgateway-`).
383* While configurable, the default {un,}marshaling uses
384[jsonpb](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/golang/protobuf/jsonpb) with
385`OrigName: true`.
386
387# Contribution
388See [CONTRIBUTING.md](http://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
389
390# License
391grpc-gateway is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License.
392See [LICENSE.txt](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/LICENSE.txt) for more details.
View as plain text